Taiwan Earthquake Response: Lessons Learned from Recent Events
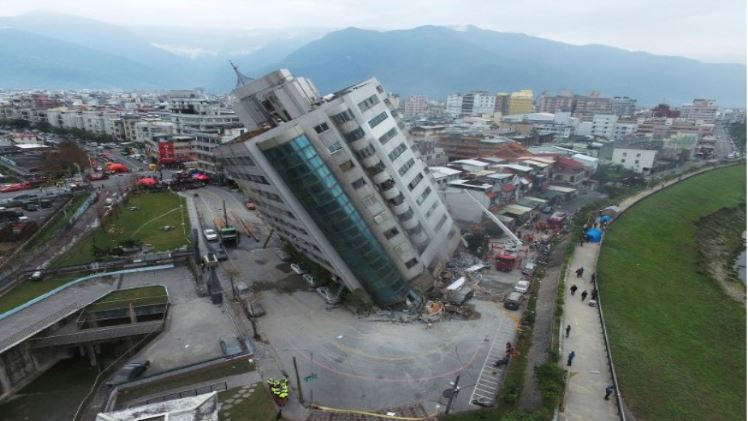

Taiwan, located on the Pacific “Ring of Fire,” is a hotspot for seismic activity, experiencing frequent earthquakes that shape its landscape and impact its people. This article delves into the geological dynamics of Taiwan, historical earthquake events, and the measures taken to mitigate risk and manage disaster response.
Geographical Setting and Seismic Activity
Taiwan’s position along the convergence of the Eurasian and Philippine Sea plates makes it particularly susceptible to earthquakes. The island is part of the complex tectonic boundary that includes the collision and subduction of these plates, leading to significant seismic activity. The continuous pushing and pulling forces not only trigger earthquakes but also contribute to Taiwan’s mountainous topography, which is still evolving.
Historical Earthquakes in Taiwan
Over the years, Taiwan has witnessed several devastating earthquakes. One of the most significant was the 1999 Jiji earthquake, also known as the 921 earthquake. This 7.6 magnitude earthquake caused immense damage, including thousands of collapsed buildings and the tragic loss of over 2,400 lives. It was a wake-up call for Taiwan, highlighting the urgent need for improved earthquake preparedness and building standards.
Advances in Earthquake Preparedness
Following the 1999 disaster, Taiwan significantly advanced its earthquake preparedness strategies. The government and local authorities have strengthened building codes, ensuring that new structures can withstand significant seismic forces. Older buildings and infrastructures have also been retrofitted to reduce the risk of collapse. Moreover, Taiwan has developed one of the world’s most advanced earthquake early warning systems, which provides crucial seconds for people to take cover before the shaking starts.
Earthquake Engineering and Building Resilience
Taiwan has become a leader in earthquake engineering, adopting innovative construction techniques designed to absorb and dissipate seismic energy. Techniques such as base isolation and the use of flexible building materials have become standard practices in areas prone to seismic activity. These technologies allow buildings and bridges to withstand the initial shocks and aftershocks of an earthquake, minimizing damage and saving lives.
Public Awareness and Education
Public education plays a vital role in earthquake preparedness in Taiwan. Schools regularly conduct earthquake drills, teaching students how to “Drop, Cover, and Hold On” during seismic events. Public awareness campaigns emphasize the importance of emergency preparedness, including having survival kits and understanding evacuation routes. The government also uses social media and mobile apps to disseminate information quickly during an earthquake.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant advancements, challenges remain. Urban areas, particularly Taipei, are densely populated and highly developed, which complicates disaster response and recovery efforts. The challenge is not only to continue improving structures but also to manage the logistics of rapid urban response. Additionally, researchers are continuously working on improving the accuracy of early warning systems and understanding the seismic risks associated with less active faults.
International Collaboration and Scientific Research
Taiwan collaborates internationally to enhance its seismic research and monitoring capabilities. Partnerships with countries like Japan, which also faces significant seismic threats, have led to advancements in technology and methodologies. Taiwanese researchers contribute to and benefit from global seismic networks, sharing data and insights that improve earthquake prediction and response strategies worldwide.
Strengthening Resilience Through Science and Preparedness
The reality of living with frequent earthquakes has shaped Taiwan into a resilient society that values preparedness, innovation, and community. Continued investments in technology, infrastructure, and public education are critical to minimizing the impact of future earthquakes. By understanding the risks and actively preparing for them, Taiwan not only protects its citizens but also provides a model for earthquake preparedness and response that other countries can follow. As seismic activity continues to pose a threat, the lessons learned in Taiwan will remain vital for enhancing global resilience against earthquakes.
Enhancing Disaster Response and Relief Efforts
In addition to strengthening buildings and infrastructure, Taiwan has refined its disaster response and relief operations over the years. The island has established a rapid deployment system for emergency services, which includes medical aid, search and rescue teams, and temporary shelters equipped to handle large-scale disasters. This coordinated approach ensures that help reaches affected areas swiftly, reducing the potential for casualties and accelerating the recovery process.
Community Involvement in Earthquake Safety
Community involvement is another critical aspect of Taiwan’s earthquake readiness. Local communities participate actively in earthquake preparedness through community-based training programs that teach residents how to respond effectively during and after earthquakes. These programs, often organized by local government agencies or non-governmental organizations (NGOs), empower residents with the knowledge and skills necessary to assist in rescue operations and provide immediate relief to neighbors in need, fostering a strong sense of solidarity and resilience among community members.
Investing in Technology and Innovation
Taiwan continues to invest heavily in technology to enhance its earthquake preparedness. Researchers are developing more sophisticated seismic monitoring tools that can provide even earlier warnings of potential earthquakes. Innovations in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being applied to better predict earthquake patterns and potential impacts, helping to refine evacuation plans and emergency responses. These technological advancements not only improve safety measures but also contribute to the economic stability by minimizing the financial impacts of disasters.
Urban Planning and Seismic Risk Management
Urban planning plays a pivotal role in managing seismic risk, particularly in densely populated cities like Taipei. The government’s urban pwvip4d development policies now require that new constructions and city planning initiatives integrate seismic risk assessments from the outset. This approach includes zoning laws that prevent construction in high-risk areas and the development of open spaces that can serve as gathering points or helipads during emergencies. By incorporating seismic considerations into urban planning, Taiwan reduces vulnerabilities and enhances overall community resilience.
International Disaster Recovery and Humanitarian Assistance
Taiwan also extends its expertise and resources internationally, providing disaster recovery and humanitarian assistance to other countries affected by earthquakes. This international aid not only helps countries in need but also strengthens Taiwan’s global relationships and reaffirms its commitment to international cooperation in disaster management. Through these efforts, Taiwan has positioned itself as a global leader in earthquake response and recovery, sharing best practices and learning from the experiences of others.
Strengthening Public Infrastructure
Public infrastructure such as transportation networks, utilities, and communication systems are also crucial in earthquake-prone regions. Taiwan has focused on making these systems more resilient to earthquakes. This includes reinforcing bridges, tunnels, water supply systems, and power plants, ensuring that they remain operational during and after an earthquake. Continuous improvements in these areas help mitigate the disruption of essential services, which is vital for emergency response and for maintaining normalcy in the aftermath of a seismic event.
A Model of Seismic Preparedness
Taiwan’s comprehensive approach to earthquake preparedness, from scientific research and innovative engineering to community education and international cooperation, serves as a model for other earthquake-prone regions. By addressing the challenges of seismic activity through multiple facets, Taiwan not only enhances its own resilience but also contributes significantly to global efforts in disaster readiness and mitigation. The lessons learned and technologies developed by Taiwan in earthquake preparedness are invaluable assets that can benefit the entire Ring of Fire and beyond, promoting safer and more resilient communities worldwide.